Welcome to the Ultimate Core Java Interview Questions and Answers Guide!
Whether you’re an experienced Java developer or just starting your career in Java programming, this resource is tailored to help you succeed in your interviews and strengthen your understanding of key Java concepts.
We have compiled a list of frequently asked Java interview questions, designed to cover a wide range of core Java topics. Top Core Java Interview Questions You Must Know in 2025 | Essential Java Interview Questions for Developers (2025 Edition) | Java Interview Questions for Freshers and Experienced Developers (2025) | Master Core Java Interview Questions and Answers (2025) – Ultimate Guide to Success. Our goal is to provide comprehensive Java interview questions and answers for developers at all levels, including beginners with experience developers.
Key topics include:
- Java basics
- Object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in Java
- Core Java interview questions for different experience levels
- Core Java syllabus and essential topics
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is Java?
Java is a high-level programming language created by James Gosling in 1991. It enables developers to create software that runs across various platforms and devices, including websites and mobile applications.
2. What are the Features of Java? Imp Questions for Fresher
Simple: Java is easy to learn and use. It’s based on C++, but without the confusing parts like pointers.
Object-Oriented: Everything in Java is organized as objects and classes, which makes coding cleaner and easier to manage.
Platform Independent: You can write Java code on one computer, and it will run on any other computer that has Java installed. This is known as “Write Once, Run Anywhere.”
Secure: Java has built-in security features that help protect your computer and data from harm.
Robust: Java is reliable. It takes care of memory and handles errors well, which makes programs less likely to crash.
Multithreading: Java can handle multiple tasks at once, which helps make programs run faster, especially for things like games and web servers.
Portable: Java programs can run on different types of computers without needing to be changed. The same program can work on Windows, Mac, or Linux.
High Performance: While Java is not as fast as some other languages, it does a good job of speeding things up while it runs.
Distributed: Java is great for networked environments. It helps programs talk to other computers over the internet or a local network.
Dynamic: Java can adapt while it’s running, like loading new classes or changing behavior, without restarting the program.
Architecture Neutral: Java is designed to work on any computer system, no matter what kind of hardware is used.
3. What is OOP(Object-Oriented Programming)? Imp Questions for Fresher
OOP stands for Object-Oriented Programming. It focuses on creating programs using classes and objects. Java OOP is a way of writing programs using objects. Here are the 6 main concepts:
Class: A class is like a blueprint for creating objects. It defines what the object will look like and what it can do (its properties and actions).
Object: An object is an instance of a class. Think of it as something you create using the class blueprint. For example, if you have a Car class, you can create different car objects like myCar or yourCar.
Inheritance: Inheritance allows one class to inherit properties and behaviors from another class. This helps in reusing code. For example, a Bike class can inherit from a general Vehicle class, so you don’t have to write common code again.
Polymorphism: Polymorphism means the ability to take many forms. In Java, you can use the same function name to do different things, depending on the object calling it.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation is about hiding the internal details of an object and only exposing the necessary parts. You protect data by using private variables and provide access through public methods.
Abstraction: Abstraction means focusing on the important things and ignoring the unnecessary details. In Java, you can use abstract classes or interfaces to define the important behaviors without worrying about how they are implemented.
4. What is a Constructor?
A constructor is a special method used to initialize objects in Java. It shares the class name, has no return type, and cannot use keywords like abstract, static, or final.
Types of Constructors:
- Default Constructor: Parameter-less constructor that initializes default values.
- Parameterized Constructor: Accepts parameters to initialize objects with specific values.
Constructor Chaining:
This refers to one constructor calling another. It can happen within the same class using the this keyword or between different classes using the super keyword.
5. What is an Abstract Class?
An abstract class in Java is a class that contains abstract methods (methods without a body) as well as concrete methods. It provides partial abstraction and is used to define common behavior for subclasses.
Achieving Abstraction:
- Abstract Class: Offers 0-100% abstraction.
- Interface: Offers 100% abstraction.
6. What is Association and Composition?
Association refers to relationships between two or more objects. It comes in two types:
- Aggregation: A weak relationship where objects can exist independently (e.g., Student and College).
class Student {
int id;
String name;
String school_name;
//create constructor
System.out.println(“\nStudent name is “ + name);
System.out.println(“Student Id is “ + id);
System.out.println(“Student belongs to the “ + school_name + “School”);
}}
class school {
String schoolName;
int noOfStudents;
// create constructor
}
public class AggregationClass
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student n1 = new Student(1, “Shekher”, “Galgotia”);
Student n2 = new Student(2, “Trilok”, “IEC”);
Student n3 = new Student(3, “Aryan”, “ABC”);
}}
- Composition: A strong relationship where one object cannot exist without the other (e.g., Department and College).
Benefits of Association:
- Code reusability
- Cost-effectiveness
- Reducing redundancy
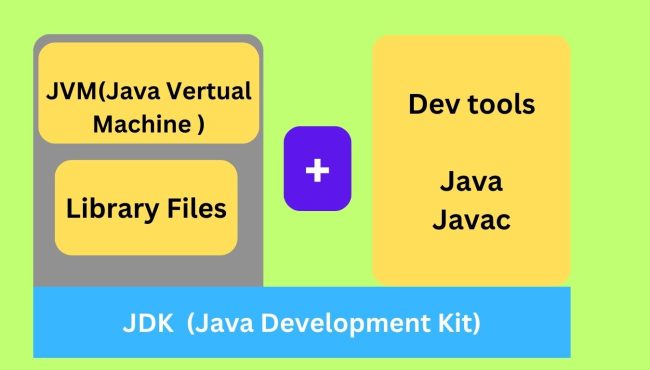
7. What is JDK? Very Imp Questions for Fresher
The JDK (Java Development Kit) is a software development kit used to develop Java applications. It includes tools like the Java compiler, Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and APIs needed to create and run Java programs.
JDK (Java Development Kit):
The JDK is a software package used by developers to build Java programs and applications. It includes development tools like the Java compiler (javac), the Java runtime (java), and documentation tools (javadoc), among others.
JRE (Java Runtime Environment):
The JRE is a software package used by clients who run Java applications but don’t develop them. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and Java libraries, allowing Java programs to execute on various platforms.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine):
The JVM is responsible for converting Java bytecode (from .class files) into machine code that can be executed by the host system. It acts as an interpreter between the compiled Java code and the machine’s operating system.
8. What is JVM and How Does it Work (Architecture)? Very Imp Questions both Fresher & Experience
The JVM is a crucial component of Java’s platform independence. It handles the execution of Java programs by interpreting compiled bytecode and managing system resources. Key components of the JVM architecture include:
- Class Loader: Loads class files into memory.
- Memory Management (Heap, Stack): Allocates and manages memory for objects and variables.
- Execution Engine: Converts bytecode to machine-specific code and executes it.
- Garbage Collector: Automatically removes unreferenced objects from memory to improve performance.
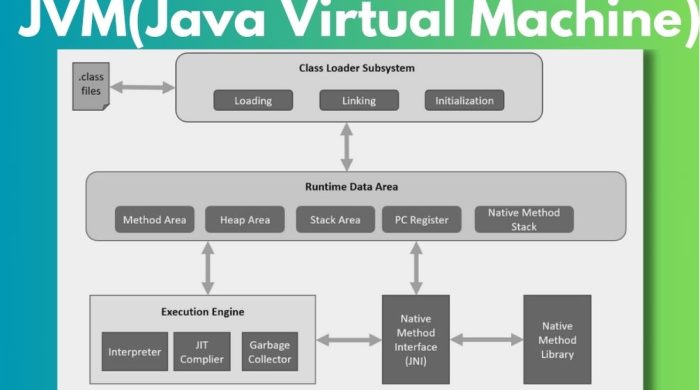
JVM (Architecture): JVM have 3 Parts
a). Classloader:
Class loader is a subsystem of JVM used to load class data. Whenever we run a Java program, it is first loaded by the class loader. There are 3 classes of functions in Java.
1. Bootstrap ClassLoader: It loads the all core related jar files to run the particular program or application.
2. Extension ClassLoader: Installs jar files to $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext directory..
3. Application ClassLoader: It’s loads the .class files from classpath.
b). Memory:
1) Class(Method) Area: it contains the class level variables and methods of class.
2) Heap: It contains java objects of a class.
3) Stack: It contains the local variables of a class.
4) Program Counter Register: It is contains the address of current executed instruction of JVM.
5) Native Method : It contains all the native methods, which is used to communicate Java to other languages.
c). Execution Engine: It contains
1.A virtual processor
2). Interpreter: it convert .class files into Machine or output language.
3). Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler: It is another compiler, Which is use to increase the speed of Interpreter.
d) Java Native Interface:
Java Native Interface (JNI) is a framework which is used to communicate with another language like C, C++, .net, Python extra.
8:What are the primitive and Non primitive data members in java?
Primitive: Which is already define by technology, that is known as primitive data members. There are 8 types primitive data member in java.
Example: Byte , short , integer, long , char , Boolean , float, double
Non primitive: –Which is manually created by developer. Exam: Array , String
9: What are the Important Java Keywords ? (Most Imp Question)
I) Static keyword : We have static to save the memory and we don’t need create object and also Static always invoke at class-Loading time so it will print things before main () .
Static keyword used with variable, method and block.
Note: It is share only one time memory.
10: What is static variable? (Most Imp Question)
If a variable is static then it will share all Objects of that class. You just need one time write one time and It will share
Exam: static collage-Name = “IEC engg & Technology, Noida” so this object(collage Name) will share with all students objects.
11: What is static method?
A static method means you don’t need to create a Object to call the static method, it is directly call by class name.
Exam– b Main method of class is a example of static method so don’t need create a object to call this main method, JVM call itself.
public static void main(String[] args) {}
12: What is the static block?
Static block initialize the static data member within a class.
class StaticBlock_Demo {
static { System.out.println(“This is static block”); }
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(“”);
}}
int age;
String name;
Student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(age + ” “ + name);
}}
class ThisKeyword_Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(25, “ankit”);
Student s2 = new Student(30, “sumit”);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}}
21). Super Keyword: The use of super keyword is, to get the property of Parent class into Child class by forcefully.
Suppose if you get your parent property forcefully then you can get by super keyword in java.
22). Final Keyword: Final keyword use to restrict the user accessibility( means you can’t access that variable for perticular task).
It restrict the access by 3 types in Java:
23). Volatile keyword: If you make a variable volatile, it means it will save in main memory. Benefit is that if 2 or more thread are using same variable form cache memory may some thread modify the value of variable and that variable is accessing by multiple thread, so it will effect to other thread values.
Note: Variable was made as thread safe by using this keyword.Variable was made as thread safe by using this keyword.This keyword also used to make Variable as thread safe.